Introduction:
In this project, you’ll learn how to use the data in your programs to make decisions about what to do.
Step 1: Asking a question
Activity Checklist
Let’s start by writing a very simple quiz program, which asks the player a question, and shows them a smiley face if they input the correct answer.
print("In Python, what do you call a 'box' used to store data?") answer = input() if answer == "variable": print(" :) ") print("Thank you for playing!")When writing this program, you’ll need to add a colon (
:) to the end of the lineif answer == "variable":, and indent the line below it (move it to the right), by pressing the Tab key (to the left of the ‘Q’ key on the keyboard).Once you’ve written the program above, try it out twice - once getting the question right, and once getting it wrong. Notice that you don’t see a smiley face unless you get the answer right.
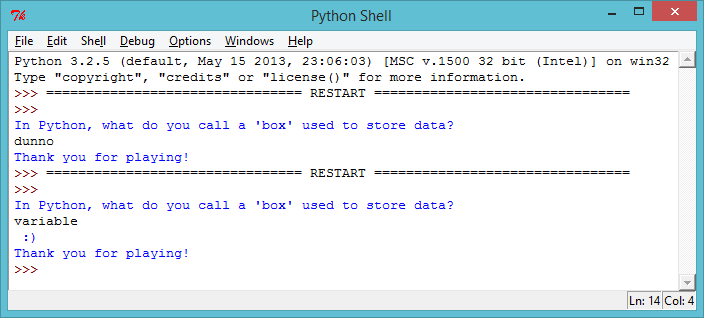
screenshot This program only runs the indented code (the code that prints the smiley face) if the answer is correct. Notice that the text “Thank you for playing!” isn’t indented, and so is printed every time, whether the answer is right or wrong.
Python uses 2 equals signs
==to check if 2 things are the same. This is because one equals sign=is used to store something in a variable (for exampleanswer = input()).The program above prints a smiley face if the player gets the question right, but doesn’t print anything to tell them they got the answer wrong. You can use an
elsestatement to print a sad face if the user inputs anything other than the correct answer.print("In Python, what do you call a 'box' used to store data?") answer = input() if answer == "variable": print(" :) ") else: print(" :( ") print("Thank you for playing!")Try out this new program, and you can see that unless you enter the correct answer, a sad face is printed.
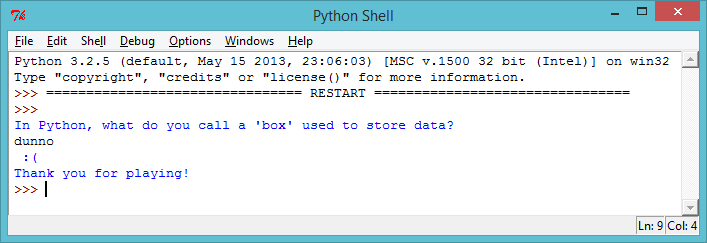
screenshot
Save Your Project
Challenge: Question time
Use what you’ve learnt so far to create your own quiz. You can choose any topic you like, and your quiz should use if and else statements to let the player know how they’re doing.
Save Your Project
Step 2: Testing
It’s always a good idea to test your programs, to make sure that they work properly.
Activity Checklist
If you’ve tested your quiz, you may have you noticed that it’s possible to get a sad face even when you input a correct answer! Like in this example, where the player has accidently presSED CAPS LOCK!
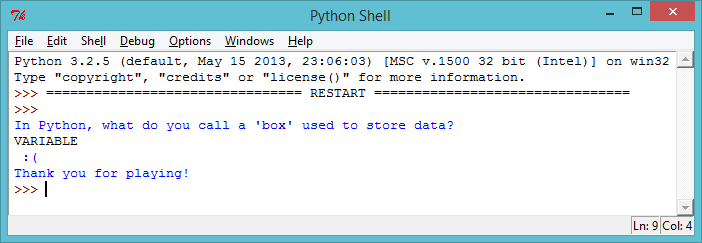
screenshot This happens because Python is very strict when it compares the player’s answer to the correct answer. To Python, “V” isn’t the same as “v”, and so if your player uses any capital letters in your answer, Python thinks the answer’s wrong!
Test this out in your game, to see if the same thing happens.
To fix this problem, all you need to do is convert whatever the player inputs into lower case, so that there are no capital letters in the player’s answer. Make this change to the line where the player inputs their answer:
answer = input().lower()Now test your quiz again. Have you fixed the problem?
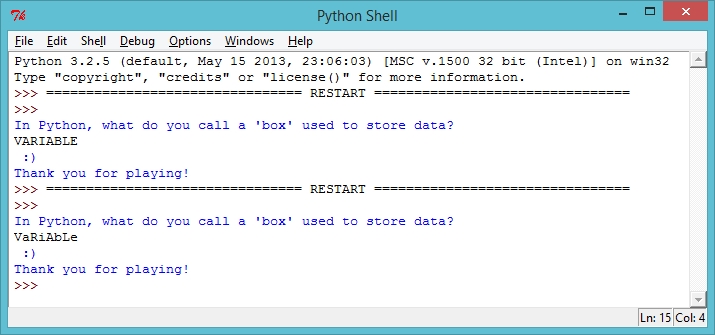
screenshot
Save Your Project
Challenge: Fixing your quiz
Make sure that your quiz always prints the right message, even if the player inputs capital letters.
Save Your Project
Step 3: Multiple choice
Activity Checklist
So far you’ve used
ifandelseto let the player know if they got the answer right or wrong. But what if you wanted a multiple choice question, where the user could see one of 4 messages? You can use anelifstatement to do this.print(''' Q1 - In Python, what do you call a 'box' used to store data? a - text b - variable c - a shoe box ''') answer = input().lower() if answer == "a": print(" Nope - text is a type of data :( ") elif answer == "b": print(" Correct!! :) ") elif answer == "c": print(" Don't be silly! :( ") else: print(" You didn't choose a, b or c :( ")elifis short for “else if”. So in the program above, the player sees one of 4 messages, depending on what they entered for their answer.Add the code above to your quiz, so that you have a multiple choice question.
Test this new question 4 times, so that you see each of the 4 messages.
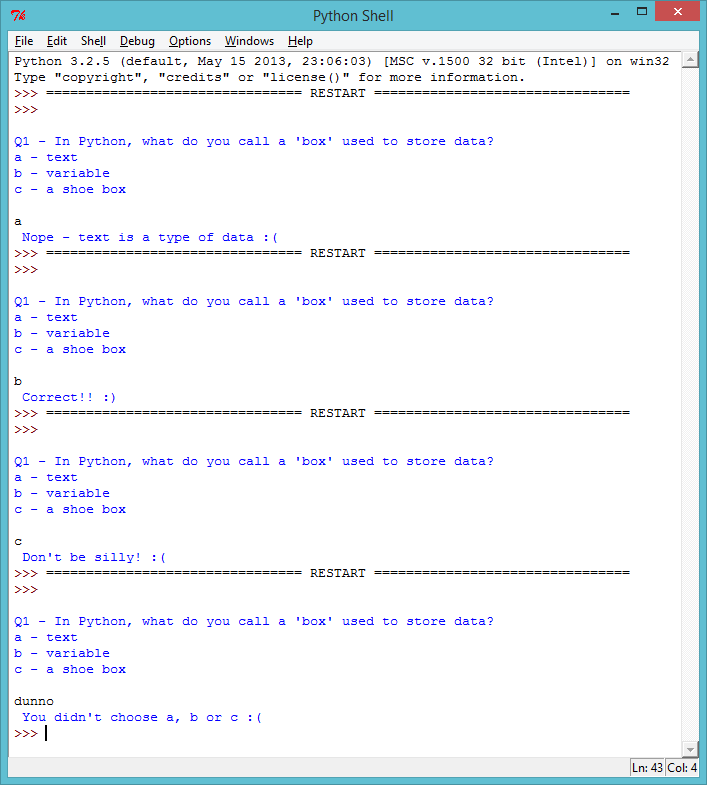
screenshot
Save Your Project
Challenge: Multiple choice quiz
Add a few multiple choice questions to your quiz program. Once you have finished making your quiz, get someone else to play it! How did they do? Did they enjoy it? Was it too easy or too hard?
Save Your Project
Challenge: Keeping score
Can you use a score variable in your quiz program, to keep track of the player’s score? This is how the variable could be used: + At the start of the program, set the score to 0. + Whenever a question is answered correctly, add 1 to their score. (score = score + 1) + Print the player’s score at the end of the quiz.
Save Your Project
Challenge: How did I do?
Can you print a personalised message to the player at the end of the game? + Say “well done” if they got all of the questions right. + else say “try again” if they got any wrong. (You’ll need to use your score variable to decide which message to print!)